
įind we need to find the height using Pythagoras’ Theorem. To find the area of the rectangle, use the formula. Example 2:įind the area of a rectangle given that the diagonal is 5cm long and the length is 4cm long. Now we can use to find the diagonal, given that l=10 and w=2. Example 1:įor example, find the diagonal of a rectangle with area 20 m 2 and length of 10 m.įirst divide the area by the length to find the width. Then use the Pythagorean Theorem, d = √(l² + w²), to calculate the diagonal of the rectangle.

These two sides are the length (l) and the width (w). If the area and one side of a rectangle are known, divide the area by the known side to find the other side.
Find diagonal of a rectangle calculator how to#
This can be written as, which equals How to Find the Diagonal of a Rectangle Given the Area If the length and width are both equal to ‘a’, then becomes. The formula for the diagonal length of a square is derived from Pythagoras’ Theorem for the length of the diagonal of a rectangle.įor a rectangle, the diagonal length is given by, where l is the length and w is the width of the rectangle.įor a square, the length and width are equal. Evaluating this, the diagonal length is 14.1cm.įormula for the diagonal length of a square with side lengths ‘a’ For example, the diagonal length of a square 10cm long is d=√2× 10. To find the diagonal length of a square, use the formula d=√2×a, where a is the side length of the square. This becomes and evaluating this, the diagonal is approximately 6.32m long. Substituting these values into the formula, we obtain.
The formula for the length of the diagonal of a rectangle Example 1:Ī rectangle has length of 6m and a width of 2m. Evaluating this, d = √40 and therefore the diagonal is approximately 6.32m long. For example, the diagonal of a rectangle of length 6m and width 2m is given by d = √(6² + 2²). The formula to find the diagonal of a rectangle is d = √(l² + w²), where l is the length and w is the width of the rectangle. Formula to Find the Diagonal of a Rectangle The diagonal is the hypotenuse of the triangle formed by dividing the rectangle in two. Given the length and width of a rectangle, the diagonal is found by squaring these values, adding them and then finding the square root of this.
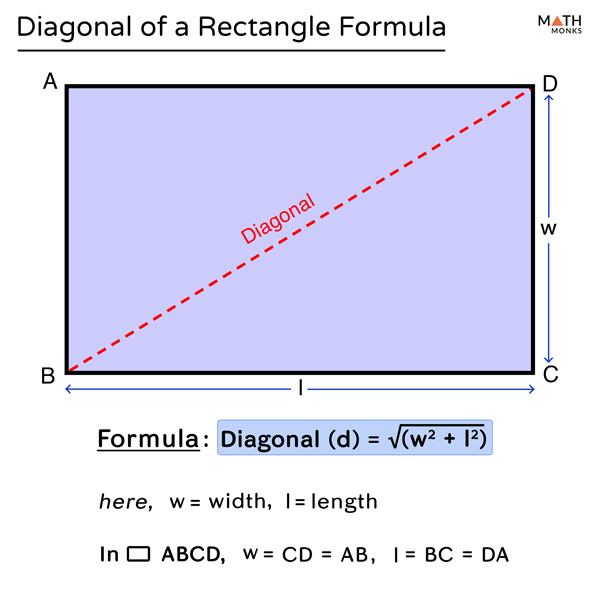
This means that the rectangle is divided into two right-angled triangles from which Pythagoras’ Theorem can be used The diagonals of a rectangle are equal in length and divide the rectangle into two congruent triangles.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
